In recent years, Generative Artificial Intelligence has increasingly become a topic of conversation among professionals and those outside the industry (who often refer to it simply as ‘artificial intelligence’). The rising popularity of the term is tied to the emergence of applications based on Generative AI, such as ChatGPT and MidJourney, among others. These applications have significantly impacted numerous professions and industries, sparking extensive controversy and discussion.
If you want to learn more about this revolutionary technology, you’re in the right place.
In this article, we’ll explain what Generative AI is and how it functions and provide practical examples of its applications, ranging from art creation to business innovation.
What is Generative Artificial Intelligence?
Let’s start with the basics. Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI, GAI) is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new content. As its name suggests, GenAI specializes in generating various types of content, including images, text, music, and even video. It accomplishes this by utilizing advanced machine learning models like neural networks. These models are trained on existing data sets and then used to generate new, unique results.
How does it work? A Generative AI-based system analyzes extensive data sets to learn underlying patterns and structures. Once it understands these patterns, the system can create content, often yielding surprising and innovative results.
How Does Generative AI Work?
To get a clearer picture of how Generative AI works, let’s walk through its process step by step. Imagine we’re creating a virtual tour guide that tailors itself to match each tourist’s unique preferences and interests.
- Data Collection: Our virtual guide begins with an extensive collection of tourist information. It includes popular attractions, hidden gems, local culinary delights, cultural highlights, and reviews from past travelers. Additionally, it involves analyzing user preferences and behaviors, which could be derived from their previous trip histories, search queries, or travel reviews.
- Training the Model: The Generative AI model is then trained to understand the vast range of travel experiences and user preferences. It learns to discern which combinations of attractions and activities are most appealing to different types of travelers.
- Content Generation: After training, the model can generate personalized travel guides. For a history enthusiast visiting Rome, it might suggest an itinerary that includes not just the Colosseum and Roman Forum but also lesser-known ancient sites. For a gastronomy lover, it could focus on top restaurants and unique local dishes.
- Optimization and Customization: But AI doesn’t stop there. This virtual guide is always learning and improving, based on what travelers are actually enjoying. If someone’s really into contemporary art, the AI can tweak their tour as it happens, suggesting the latest gallery openings or art shows.
Examples of Generative AI Applications

- ChatGPT: an advanced chatbot built on the GPT language model, renowned for its ability to engage in fluent, human-like conversations. ChatGPT goes beyond just answering queries; it can generate a wide range of content, craft poems, assist with homework, and even write programming code.
- MidJourney: an innovative application that enables users to create sophisticated graphics and images. Utilizing Generative AI, MidJourney can convert simple text inputs into detailed and intricate visualizations.
- GitHub Copilot: a tool for developers, aiding in code writing through intelligent suggestions and autocomplete features.
- Adobe Firefly: A cutting-edge tool from Adobe that employs AI to generate graphics, fonts, and various visual elements.
The Rising Popularity of Generative AI
Generative Artificial Intelligence, despite being a relatively recent development, has rapidly gained significance and popularity in the tech world. Its market potential is particularly noteworthy.
According to projections by Statista, the generative AI market is poised for substantial growth in the near future. It’s estimated to expand at an impressive CAGR of over 24.4% from 2023 to 2030. By the end of this period, its market value is expected to reach a staggering $207 billion, underscoring the immense potential and interest in this technology.
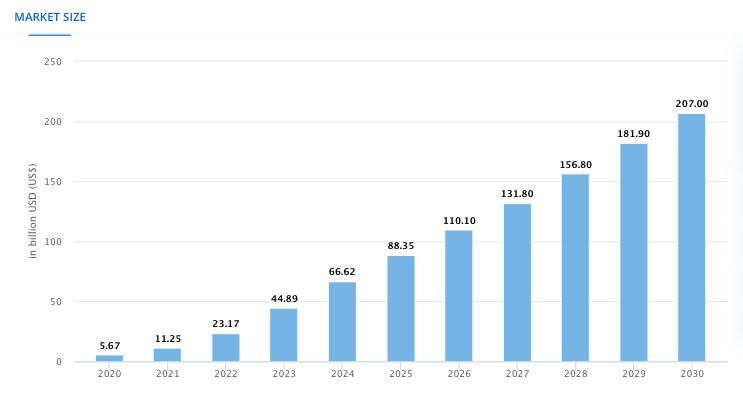
Moreover, Salesforce research indicates that three out of five employees (61%) currently use or plan to use generative artificial intelligence. These figures show how powerful this technology is and how much of an impact it has on our lives – both personal and professional.
Examples of Generative AI Applications in Various Industries
Art
In the realm of painting and graphics, programs like DeepArt use machine learning algorithms to generate paintings that mimic the styles of renowned artists. Tools such as AIVA apply AI to create musical compositions in the music industry. Moreover, there’s been notable excitement surrounding OpenAI’s latest innovation, Sora which can produce videos from straightforward text prompts. You can view the outcomes in this video:
Architecture and Design
In the field of architecture and design, Generative AI is revolutionizing the way we approach creativity, offering tools for crafting designs that are both more intricate and effective. Autodesk’s Dreamcatcher is a prime example, leveraging sophisticated algorithms to produce structural designs that seamlessly marry aesthetic appeal with practical functionality.
Marketing
Generative AI is transforming content creation and personalization in the marketing domain, elevating its effectiveness and engagement levels. Platforms like Persado leverage AI to craft compelling advertising copy, enabling highly customized messaging. Additionally, innovative image generation technologies, such as OpenAI’s DALL-E, facilitate the production of unique visuals, significantly enhancing the creative dimension of marketing campaigns.
Tourism
In the tourism sector, Generative AI is profoundly influencing travel planning personalization. Booking.com has launched a GPT-based trip planner, enabling users in the US to craft personalized itineraries through its app. Similarly, Expedia has embraced this technology to provide chat-based travel recommendations and the capability to add hotels to users’ itineraries automatically.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to GenAI
- Generative Model: A type of artificial intelligence model that is trained on data to generate new data that can mimic the original dataset.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A type of neural networks used in Generative AI, consisting of two parts: a generator that creates data, and a discriminator that evaluates their authenticity.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): An advanced artificial intelligence model, trained on vast datasets of textual data, used for creating applications for generating text, translating, answering questions, and other natural language processing tasks.
- ChatGPT: An application based on the GPT model designed for chat conversations. ChatGPT simulates natural dialogues by answering questions and performing language tasks, such as writing texts or programming.
- Fine-Tuning: The process of further training an already trained generative model on a specific, often smaller dataset to better adapt to specific requirements or tasks.
- Transfer Learning in Generative AI: A method that involves using knowledge gained by a model during training on one task to improve performance on another related task. Generative AI often involves using trained models to generate content in new contexts.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimizing the hyperparameters of a generative model, such as learning rate and number of network layers, to achieve better results.
- Model Conditioning: A technique used in Generative AI that allows controlling the data generation process by specifying conditions, such as themes, styles, or other specific characteristics of the desired content.
- Zero-Shot Learning: A machine learning method in which a generative model is capable of performing tasks on which it was not directly trained, using knowledge acquired during training on other tasks.
- Few-Shot Learning: A machine learning technique in which a generative model is trained on a very small number of examples, allowing it to quickly adapt to new tasks with limited training data.
Conclusion
As you can see, Generative AI is undoubtedly changing our reality, revolutionizing both professional and private lives. It is a tool with enormous potential across various industries, making it worthwhile to follow its development to understand how it can impact the future of our world.
To do so, you can subscribe to our newsletter, where we regularly share trends and discoveries in AI and tourism.
