While ‘natural language processing’ (NLP) may sound puzzling, we’re sure you’ve already encountered this technology. It’s the basis of voice navigation systems, speech-to-text dictation software, chatbots, search engines, and systems like ChatGPT.
Want to learn more? In this article, we’ll explain what NLP is and how it works, provide examples of its applications, and, most importantly, discuss the benefits it can bring to your business. Keep reading to discover the potential of this powerful technology!
What is natural language processing?
As always, let’s start with a definition. In a nutshell, Natural Language Processing (NLP) can be described as follows:
Natural Language Processing is a field of artificial intelligence combining programming and linguistics elements, enabling computers to understand human language.
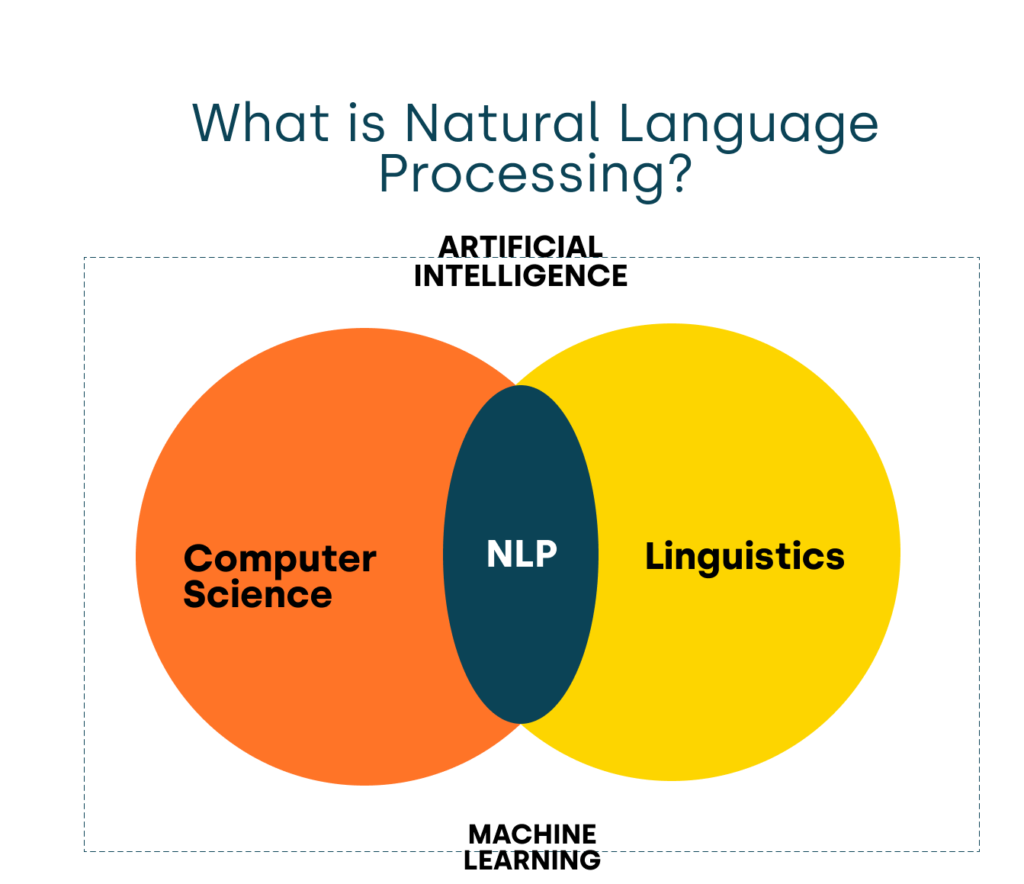
NLP utilizes advanced technologies, including computational linguistics, machine learning, and deep learning models, to process human language in various forms, from text to voice recordings. The main goal of NLP-based solutions is not just to grasp the meaning of individual words but also to comprehend entire speech patterns, considering the speaker’s context, intentions, and even emotions.
How does natural language processing work?
To better understand what NLP is, it’s helpful to see how – step by step – the process works.
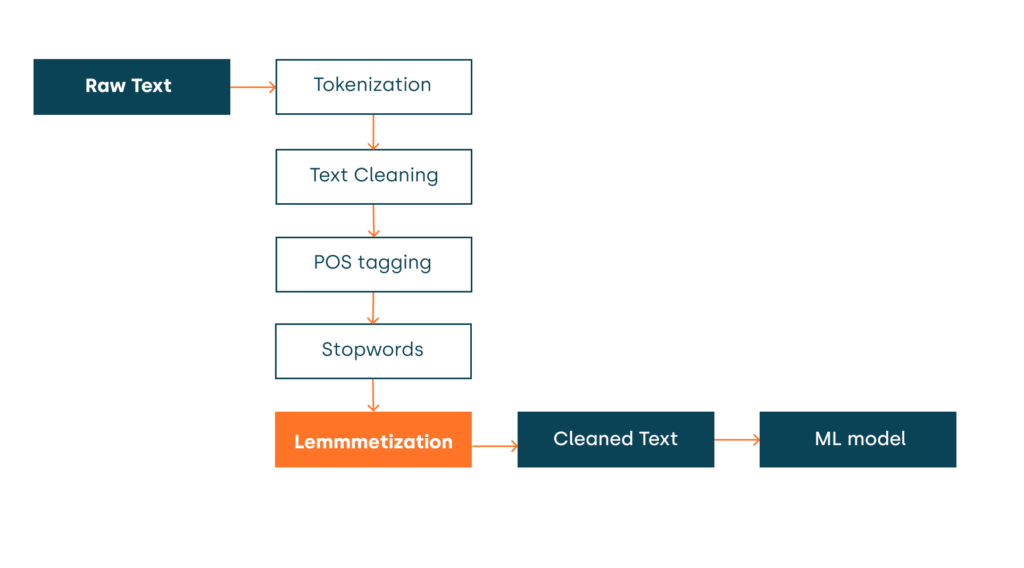
1. Data Gathering
The fundamental component of any solution based on machine learning models is data. Specifically for Natural Language Processing (NLP), these systems require a corpus – a vast collection of linguistic data. For instance, the GPT-3 version of a system like ChatGPT has been trained on approximately 570 GB of data. This data includes a diverse range of sources such as books, web texts, Wikipedia, and various articles available on the Internet, amounting to 300 billion words.
2. Converting Human Language into a Format Understandable by Computers
After data collection, the system converts this data into a numerical format, enabling it to comprehend and process the information. The conversion technique varies based on the type of data, whether text or audio. For instance, with voice data, the system analyzes and extracts information about varying frequency components at different moments in the recording.
3. Understanding the Message
Remember, while words and sentences are understandable to humans, they are merely strings of characters to computers. To enable these systems to comprehend language and the meaning of statements, AI and NLP engineers must train them accordingly.
This is where the so-called NLU (Natural Language Understanding) comes in, involving the processing of input data to make sense of sentences in natural language.
It usually involves various natural language processing techniques, such as tokenization (breaking text into smaller parts), part-of-speech tagging, and stemming (reducing words to their basic forms).
These methods allow algorithms to grasp the rules of human language, leading to an understanding of sentence structure and meaning.
There are significant challenges at this stage notably with homonyms — words that share the exact spelling or pronunciation but have different meanings. The system must discern their context when such words are encountered by analyzing the entire utterance.
4. Answer Generation
Once our system understands the questions or commands it receives, it generates an appropriate response. It is achieved through deep learning algorithms that enable it not only to read and comprehend statements but also to formulate its own responses. This process, known as Natural Language Generation (NLG), transforms structured data (data understandable to the computer) into natural language outputs that are understandable to humans.
Taking the example of ChatGPT, at this stage the system generates responses based on the user’s input. It leverages billions of previously learned words and language rules and has an extensive knowledge base. Practically, this involves predicting subsequent text segments that should logically follow the provided input, guided by established language patterns.
Below is an example of ChatGPT responding to the question, ‘What is worth seeing in Poland in November?’

5. Continuous Training and Fine-Tuning of the Model
You must constantly refine and update to ensure your system works at its best. The more data the system processes, the more accurate it becomes. It is particularly crucial for NLP solutions, where the model needs regular fine-tuning with new data alongside continuous refinement based on the feedback it receives. As a result, the system becomes increasingly precise and effective in understanding and responding to user queries.
For instance, to keep ChatGPT informed about current regulations in a specific location, it is essential to tune the model with new, up-to-date information. This ongoing training enables the AI to provide the most relevant and accurate responses.
Examples of NLP Applications
Let’s explore some examples. As mentioned earlier, many of us frequently use solutions based on NLP, often without realizing they involve this technology. Below are some of these solutions:
- Voice Assistants: NLP is crucial for Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. It enables them to understand and naturally respond to user voice queries, performing tasks ranging from setting alarms to searching for information online.
- Translators: Tools like Google Translate and DeepL employ NLP for real-time translation of texts into various languages.
- Text Dictation Function: The text dictation feature, available on smartphones and other devices, allows users to dictate text that is subsequently transcribed into written form.
- Sentiment Analysis: Companies utilize NLP to analyze customer reviews and opinions, helping them grasp the general sentiment toward their products or services. This insight aids in refining marketing strategies and enhancing customer service.
- Chatbots: Chatbots on websites and apps use NLP to respond quickly to customer inquiries.
- Search Engines: Advanced or semantic search engines apply NLP to understand the intent and context behind search queries. This capability enables them to comprehend complex queries and deliver answers that grasp the whole meaning of the search content rather than merely matching keywords.
Industries Benefiting from Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP can be used in various sectors, such as:
- Tourism: In tourism, NLP helps identify ideal travel deals and more. For instance, Qtravel Search, a travel search engine, uses NLP to comprehend user queries effectively, matching them with suitable travel deals, hotels, or attractions based on a detailed query analysis.
- Healthcare: NLP is crucial in analyzing medical records to expedite diagnoses and personalize patient care. NLP-powered systems can evaluate medical histories, doctor’s notes, and medical publications, offering vital insights to healthcare professionals.
- Finance:NLP aids in market analysis and fraud detection within the financial sector. It can process extensive financial data, including reports and market news, to provide investment recommendations or identify potential fraudulent trading patterns.
- Education: NLP is instrumental in creating personalized curricula and language learning tools. It analyzes students’ responses to tailor teaching materials to their understanding level and learning style.
- Accounting: NLP enhances accounting efficiency by automating data entry and extracting essential details from invoices, receipts, and other financial documents. This automation speeds up processes like invoice posting and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Benefits of Using Natural Language Processing in Business
Are you still wondering whether NLP is the right technology for your company? If so, you need to discover these key benefits it offers:
- Time Savings: NLP enables the automation of repetitive tasks like sorting customer service emails or analyzing market data, leading to substantial time savings for your employees.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: NLP-powered solutions like chatbots and semantic search engines deliver quick and precise responses, enhancing service quality and boosting customer satisfaction.
- Deeper Customer Insights: NLP’s ability to analyze customer feedback and reviews offers more profound insights into customer needs and preferences, allowing for more customized service offerings.
- Informed Business Decisions: NLP-driven data analysis yields accurate insights into market trends and customer behavior, aiding in more informed, data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Conversions and Sales: In marketing and sales, NLP aids in precise ad targeting and offers personalization, increasing conversion rates and sales.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to NLP
- Tokenization: Dividing text into smaller units, such as words, phrases, or tokens.
- Morphological Analysis: Examining the structure of words, focusing on elements like roots, endings, and other morphological components.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Assigning grammatical categories, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives, to each word in a text.
- Stemming: Simplifying words to their base form (e.g., “running” to “run”).
- Syntactic Analysis: Investigating the grammatical structure of a sentence and determining the relationships between words.
- Semantic Analysis: A process of understanding and interpreting the meanings of sentences.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifying and classifying key information in text, including names of people, places, and organizations.
- Language Model: A system for predicting the sequence of words or sentences based on prior examples.
- Information Extraction: Extracting pertinent information from text, such as dates, numbers, product names, etc.
- Text Classification: Categorizing text into specific groups or labels based on content.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): The process by which a machine interprets, understands, and processes human speech or text to extract meaning.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG): The creation of human-understandable text by a computer.
Conclusion
We hope this article helped you better understand natural language processing and its invaluable business potential.
If you want to implement an NLP-based solution in your company, feel free to contact our team. We will be happy to explain to you how our search engine (based on this technology) works and demonstrate how its implementation can revolutionize your business.
